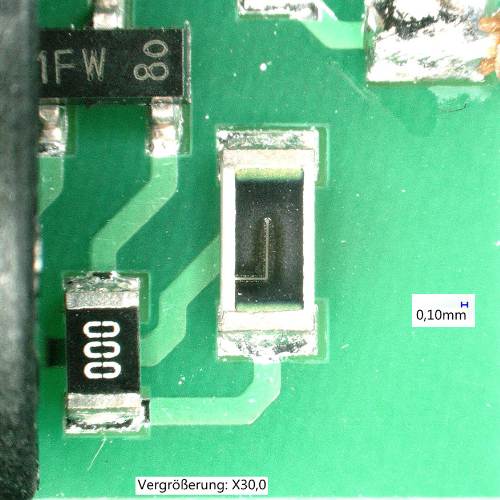
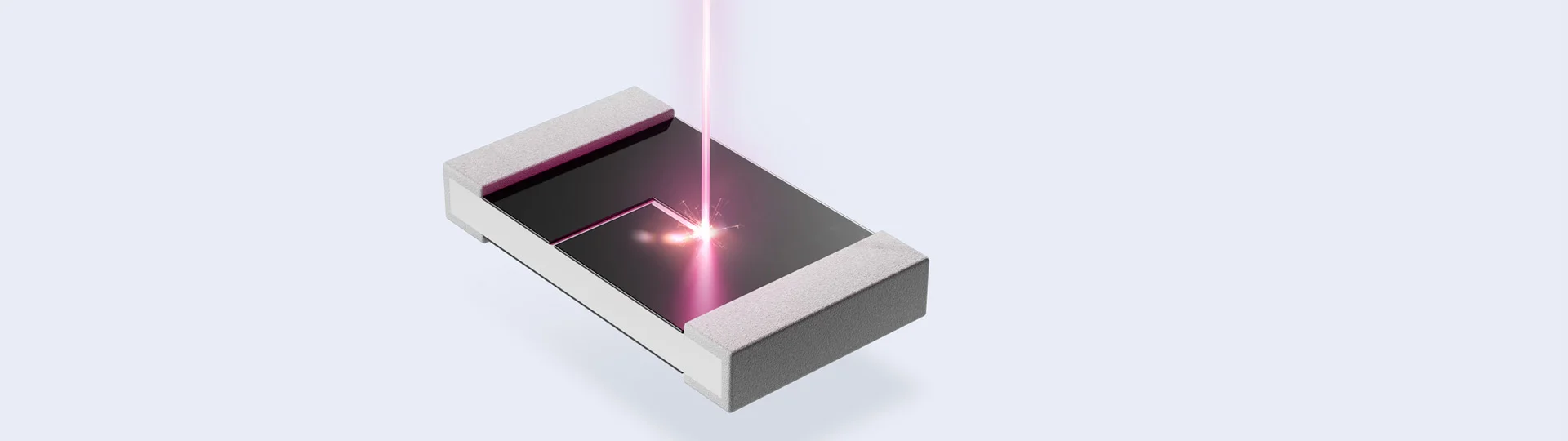
Processes – Laser Trimming
Laser trimming, also known as laser alignment, is a process in which electronic components (e.g. resistors) and circuits are aligned or trimmed using laser-induced changes. As a rule, resistors (thick and thin film) of a circuit are influenced by the laser in such a way that the individual resistance value or the entire circuit is adjusted. The prerequisite for carrying out such a laser trimming process is a suitable laser system that can be controlled with pulse accuracy by connecting it to the measurement technology. The laser system is combined with a AOI vision system to position the laser beam with high precision and thus enable excellent alignment.
Various cutting forms are used in practice for laser trimming or laser alignment. The frequently used serpentine cut is characterized by a large trimming range and advantageously replaces mechanical trimmers. In addition to the smaller size and lower costs compared to trimming potentiometers, laser-trimmed resistors are characterized by higher long-term stability. Frequent trimming applications are the characteristic curve adjustment of electronic sensors, the adjustment to the nominal switching distance of proximity switches or the linearization of measuring amplifiers in medical and measurement technology.
Laser trimming enables the precise adjustment of resistors and circuits. Individual resistors or specific areas of a circuit can be trimmed precisely by selectively deflecting the scanner mirrors of the laser. This is done without damaging the ceramic base body by removing the resistor layer or reducing the specific conductance through a laser cut.
The trimming process is monitored in real time and stopped as soon as the desired properties are achieved. The last position data achieved is automatically saved so that the trimming cut can be continued if necessary. The aim is to precisely adjust the resistance value with minimal deviations.
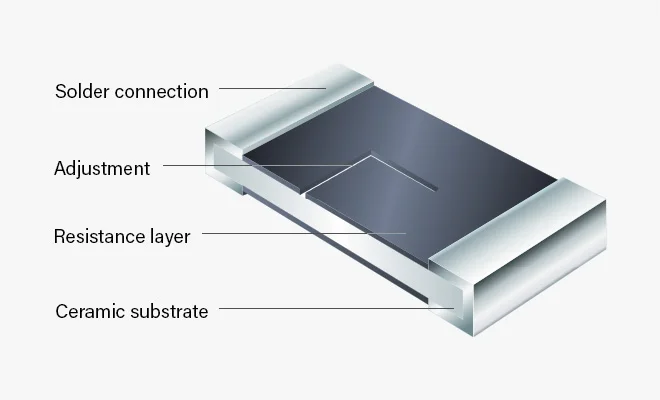
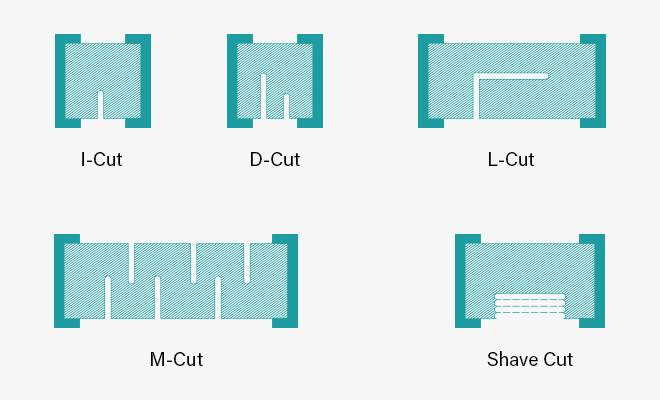
In practice, various cutting geometries are used to achieve optimum linearity of the trimming range for rectangular resistors. These proven cuts ensure that the resistance values are adjusted precisely and efficiently.
Press ENTER to confirm or press ESC to close